Buy Home Energy Monitoring System – Top Solutions, Benefits & Guide
Buy a Home Energy Monitoring System: Ultimate Guide for 2025
In an age of rising electricity costs, renewable energy, and smart homes, understanding how your home uses energy is more critical than ever. A home energy monitoring system gives you insight into your household’s electricity consumption in real time, enabling smarter decisions, cost savings, and improved efficiency. This guide covers how these systems work, the benefits, detailed product reviews, practical use cases, and step-by-step advice on how and where to buy one.
What a Home Energy Monitoring System Is
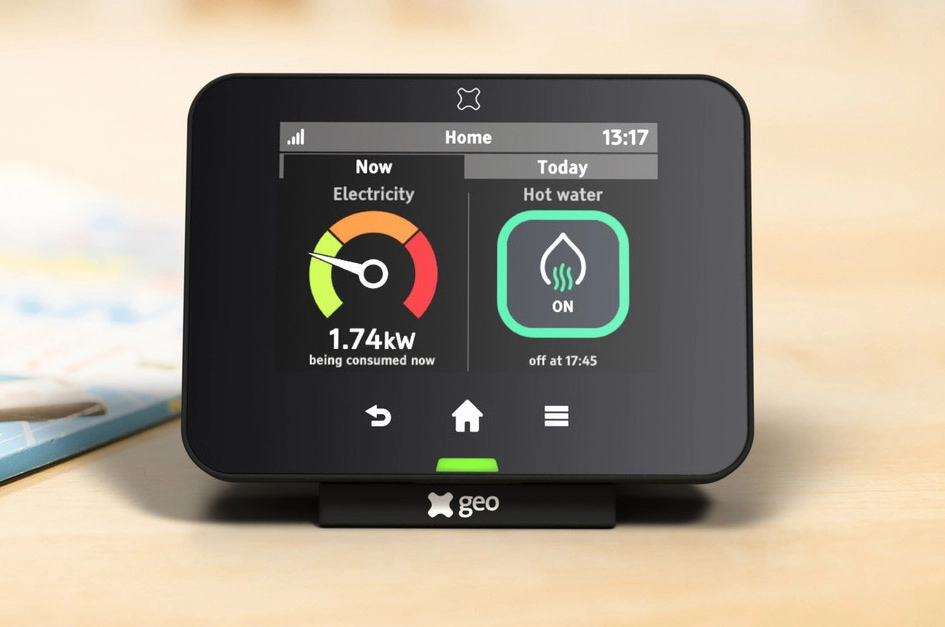
A home energy monitoring system typically consists of sensors (often current transformers or CT clamps) placed around your home’s electrical mains or individual circuits, a control or gateway module, and a software or mobile app interface that reports energy usage data in real time.
The system continuously measures voltage, current, power, and consumption, then uploads that data to the app or cloud. The app visualizes usage per circuit or aggregated, tracks trends, shows appliances’ energy draw, and alerts for anomalies.
Some advanced systems use nonintrusive load monitoring (NILM) analyzing voltage/current waveforms to disaggregate which appliances are in use, without needing a sensor on each device.
These systems are often used alongside or integrated with solar panels, battery systems, smart thermostats, or home automation platforms to optimize energy flows.
Why Invest in a Home Energy Monitoring System
Visibility & Real-Time Data
One of the core benefits is that you see exactly how much energy your home or individual circuits are consuming at any moment. This visibility helps you understand which appliances are energy hogs, what times usage peaks, or if something is running unexpectedly.
With real-time feedback, you avoid blind estimates and can intervene immediately turn off devices, shift usage, or detect leaks.
Cost Savings & Efficiency
By understanding detailed consumption, you can reduce wastage, optimize usage, and lower your electricity bill. Monitoring helps you find inefficient appliances, phantom loads, or devices running in standby mode.
Over time, many users report savings by scheduling heavy loads during off-peak hours, upgrading inefficient devices, or shutting unused circuits.
Fault Detection & Alerts
Many systems can alert you if a circuit draws more than usual (indicating a fault or failing appliance), if wiring issues arise, or if usage patterns deviate significantly from norms. This early warning can prevent breakdowns or safety hazards.
Integration & Smart Control
When integrated with smart home or energy systems (solar, battery, EV charger), the monitor can help automate load shifting, battery charging, or limit usage during high-rate periods. The system becomes a brain behind your home’s energy flow.
Behavior Change & Energy Awareness
Often just seeing consumption data leads to behavioral changes: turning off lights, unplugging idle devices, optimizing heating/cooling. The awareness itself drives reduction in wastage.
Product Examples: Top Home Energy Monitoring Systems
Below are five real-world energy monitoring devices or systems, with detailed descriptions, use cases, pros/cons, and why you might choose them.
Emporia Vue 3 Home Energy Monitor

Description & Features
Emporia’s Vue 3 monitor clamps onto your main electrical panel and provides circuit-level readings. It supports 16 individual circuit sensors and gives real-time data via its app. It can also integrate with solar generation systems.
Detailed Explanation
The Emporia Vue 3 uses CT clamps around each circuit to measure consumption. The main unit sends data to the cloud, updates your app, and shows both per-circuit and aggregated use. You can label circuits (e.g. HVAC, refrigerator) and view historic patterns.
Use Case & Problems Solved
If you want to detect which particular circuit is contributing the most to your bill (e.g., broken HVAC, inefficient appliance), this system is ideal. It solves the “which device is draining power” mystery. Many users have discovered phantom loads (devices still drawing power when “off”) using Emporia.
Why Choose It
It’s a feature-rich solution, scalable, with good app interface and community support. Great for users who want visibility down to circuit level without needing professional installation.
Shelly Pro EM
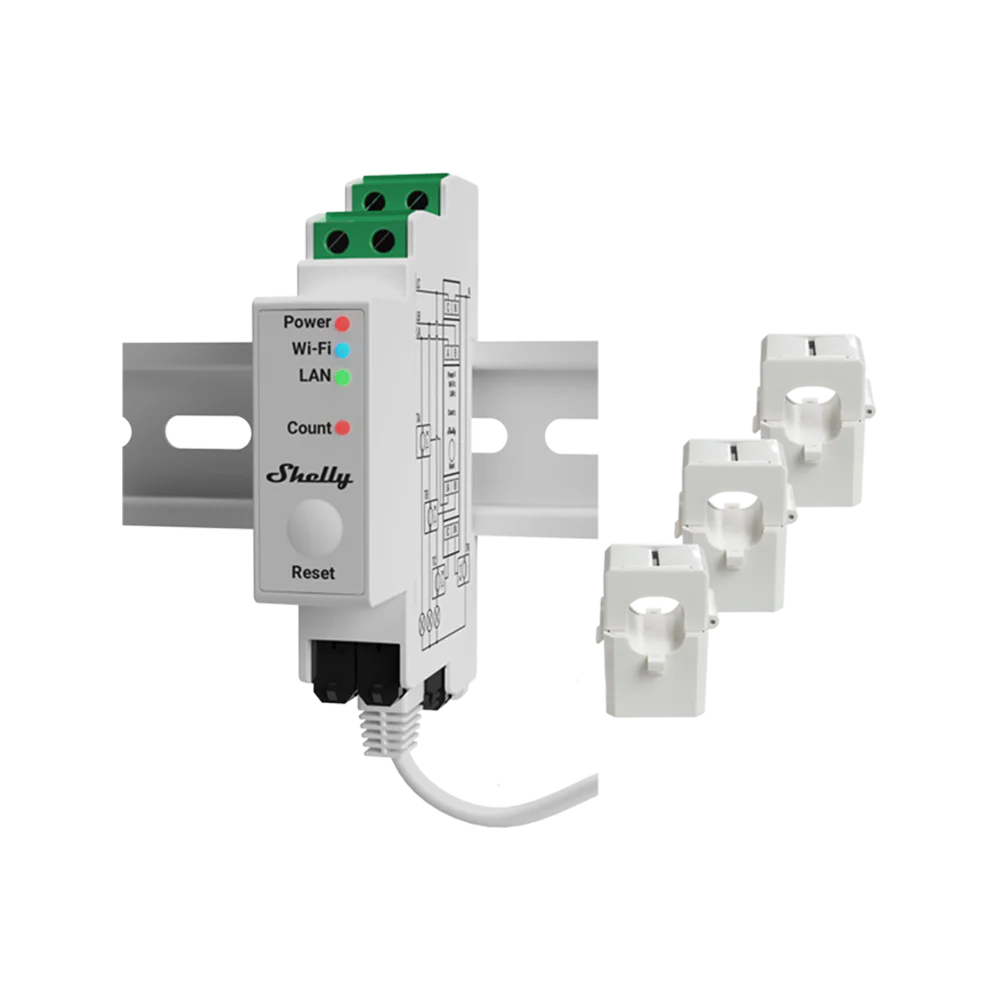
Description & Features
Shelly Pro EM is a smart energy monitor device intended to integrate into smart home setups. It supports WiFi, MQTT, has high-accuracy measurement, and can monitor multiple channels.
Detailed Explanation
You install it inside your distribution board. It monitors voltage and current and communicates via WiFi or local protocols. Because it supports smart home standards, it can be integrated into Home Assistant, openHAB, or other home automation systems.
Use Case & Problems Solved
If you have or plan a smart home platform and want your energy monitor to feed automation, Shelly Pro EM offers that bridge. It helps with automating devices when energy is cheaper, or notifying you when an appliance is acting erratically.
Why Choose It
It’s well-suited to tech-savvy users who want integration and control. The local communication support is an advantage for privacy and reliability over cloud-only systems.
Refoss Smart Home Energy Monitor
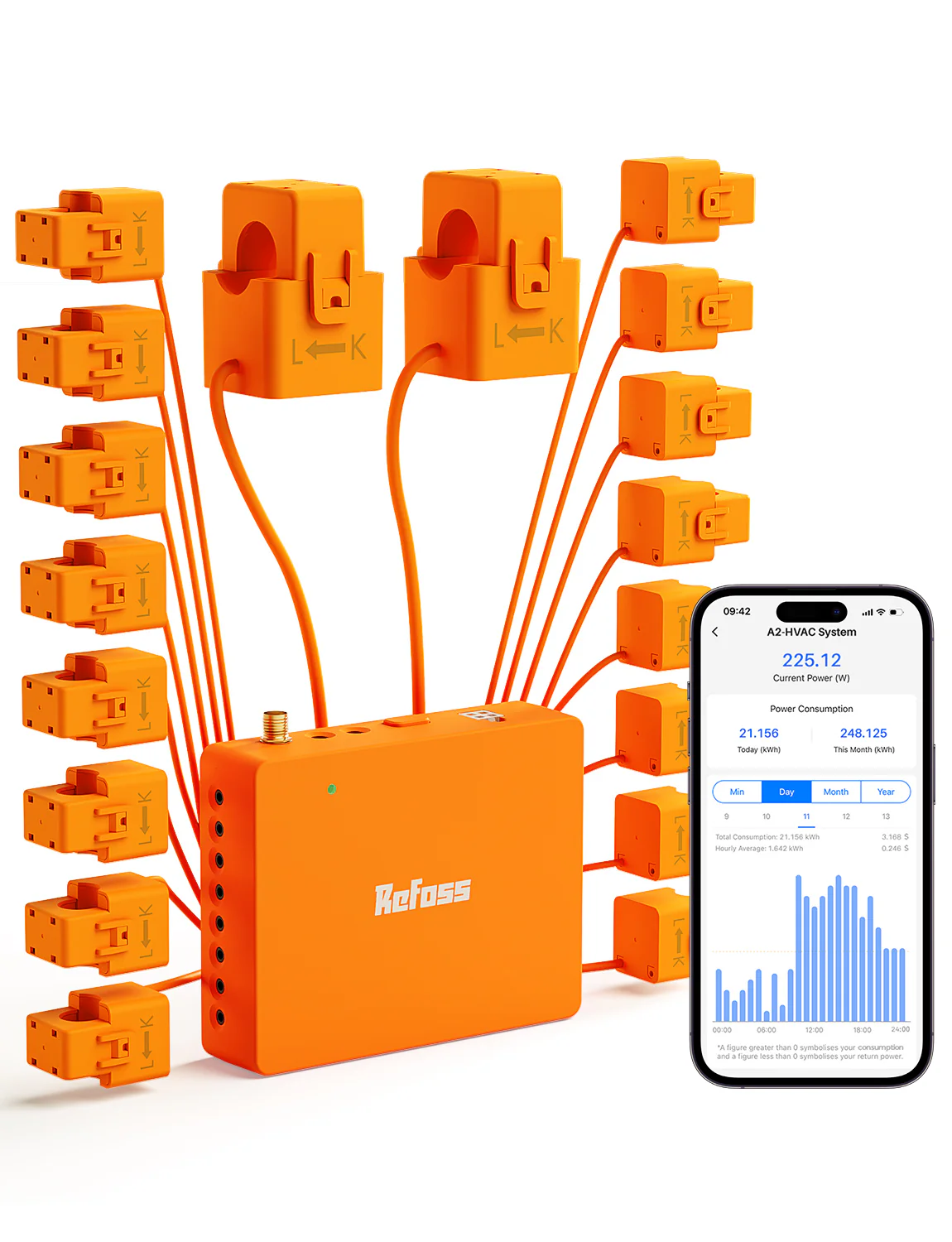
Description & Features
Refoss offers a smart home energy monitor that supports multiple channels (e.g. 16 x 60 A), real-time tracking, and integration with Home Assistant. It gives you accurate circuit-level data.
Detailed Explanation
It uses CT sensors on circuits and a central communication module. The data is relayed to the app or your home automation system. You get live power, cumulative kWh, and logging.
Use Case & Problems Solved
For homes with many circuits (multiple heavy loads), Refoss lets you monitor each one. You might discover that one HVAC system, a pool pump, or a water heater is unusually consuming and adjust accordingly.
Why Choose It
Its capacity, integration support, and reliable measurement make it suitable for larger homes or tech-driven users.
TUYA WiFi Energy Meter 63A
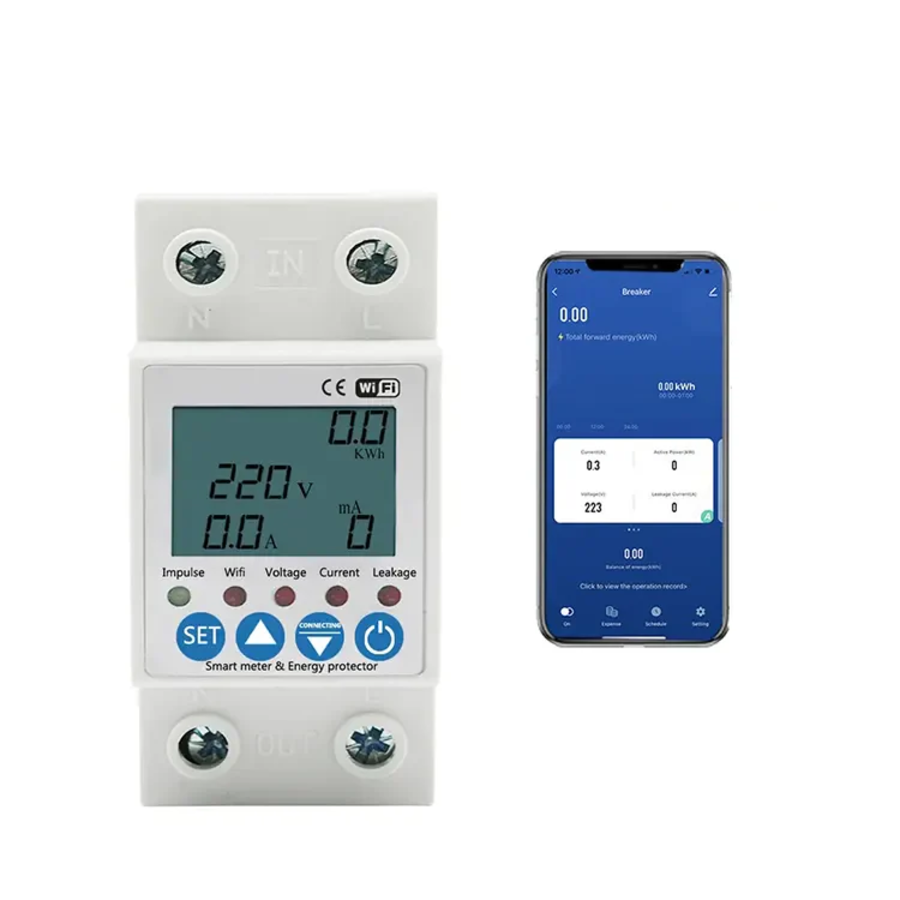

Description & Features
TUYA WiFi Energy Meter is a combination energy meter + leakage protection device supporting WiFi, typically up to 63A, measuring real-time usage, voltage, and current. It pairs with the Tuya (Smart Life) ecosystem.
Detailed Explanation
This device is installed in an electrical panel and can monitor energy and report it to a cloud app. It also includes leakage or over-current protection, adding a safety dimension.
Use Case & Problems Solved
For those wishing a low-cost WiFi-enabled energy monitor with safety features (overcurrent, leakage), this is a dual-purpose device. It’s perfect for moderate-size homes or workshops.
Why Choose It
It offers both monitoring and protection in one unit, making it efficient and compact for simpler setups.
Shelly EM Wi‑Fi Energy Meter
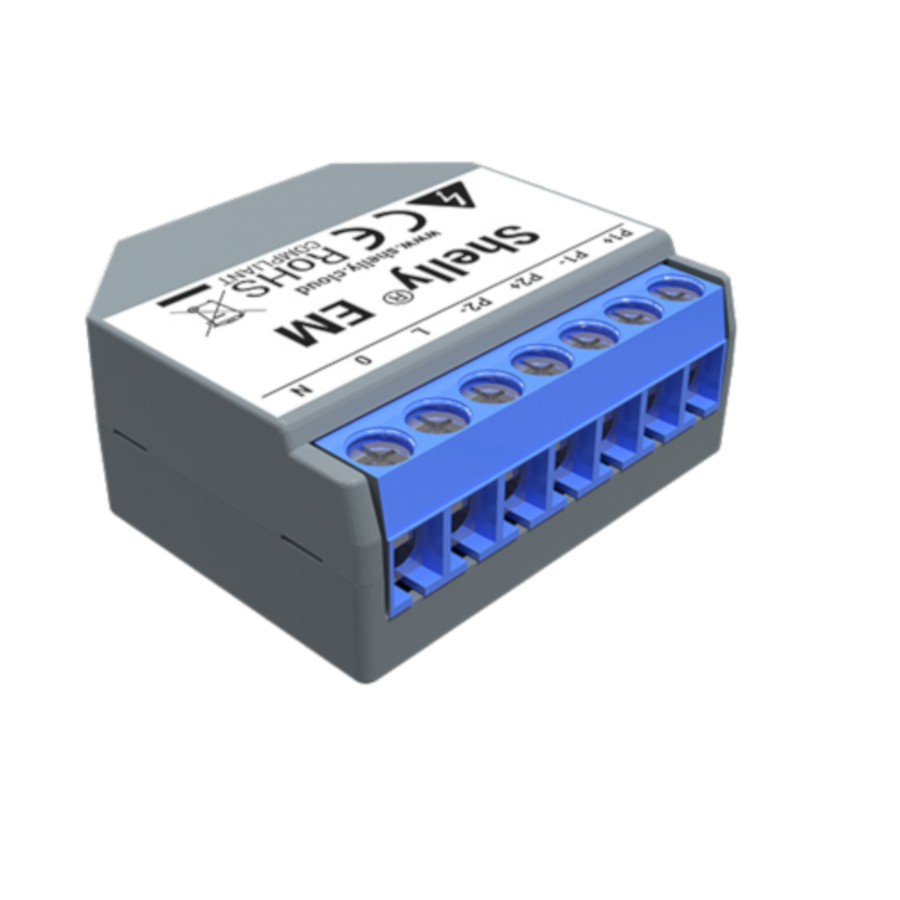

Description & Features
Shelly EM is a WiFi-enabled two-channel energy meter. It provides real-time current and voltage readings and integration with smart systems.
Detailed Explanation
You clamp it to two circuits or measure mains and one subcircuit. It reports consumption live and integrates with automation setups.
Use Case & Problems Solved
If you want to monitor two key circuits (e.g. HVAC and general load), this is a compact solution. It’s helpful if you want to catch high-draw appliances or compare consumption across circuits.
Why Choose It
Compact, smart-home friendly, and suited for users who don’t need full multi-circuit setups but want insight into critical loads.
Square D WISEREMPVZ Home Energy Monitor
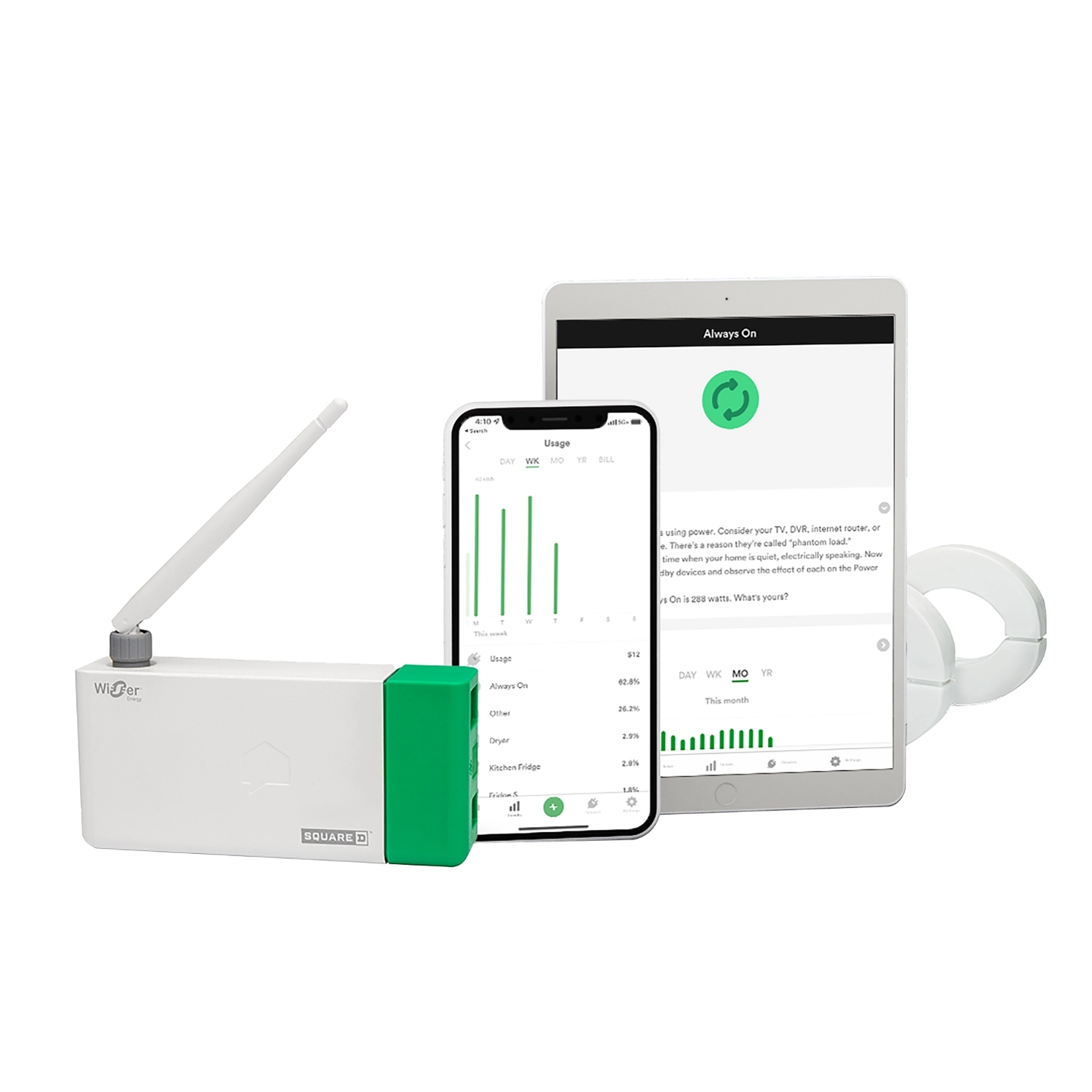

Description & Features
Square D’s WISEREMPVZ is a home energy monitor system designed to integrate with Schneider Electric’s Wiser ecosystem. It gives visibility into energy usage and load management.
Detailed Explanation
The device interfaces with main/branch circuits and reports via the Wiser app. It also supports integration with other Schneider smart home products.
Use Case & Problems Solved
If your home already uses Schneider equipment (panels, switches), the WISEREMPVZ fits smoothly. It helps manage loads and energy use in sync with other devices.
Why Choose It
The integration with a broader smart home ecosystem and brand reliability makes it compelling if your setup already includes compatible components.
How Home Energy Monitoring Systems Work (Technology Deep Dive)
The operation of an energy monitoring system involves several key components:
-
Sensors / CT Clamps – These clamps measure current (amperage) flowing through an electrical conductor, capturing instantaneous and cumulative usage.
-
Voltage Measurement – Together with current, systems derive power (Watts = Voltage × Current) and energy (kWh) over time.
-
Data Aggregation & Communication – The sensor module sends data to a gateway or hub, often via WiFi, Ethernet, or a local bus.
-
Cloud or Local Processing – Data is processed to produce graphs, trends, alerts, and sometimes disaggregated appliance usage (using NILM techniques).
-
User Interface / App – The user sees the data in real time, with historical charts, alerts, device-level breakdowns, and control or automation options.
Some systems also integrate load disaggregation (NILM) to infer usage of individual appliances without placing a sensor on each device.
In advanced homes with solar and battery systems, the energy monitor helps manage flows (e.g., when to charge battery, when to export, or when to defer consumption). It essentially acts like the brain of your home’s energy system.
Because energy use fluctuates moment to moment, high-speed sampling and accurate sensor calibration are important for useful data.
Benefits of Home Energy Monitoring Systems
Identify Energy Hogs & Reduce Waste
With detailed data, you can pinpoint inefficient appliances, devices left in standby, or circuits that draw unexpectedly. Recognizing these allows targeted upgrades or behavioral changes to cut waste.
Optimize Energy Usage & Cost
You can shift high-energy tasks (laundry, charging, electric heating) to off-peak times when rates are lower. Integration with differential pricing provides opportunity for smart scheduling.
Prevent Failures & Detect Faults
Abnormal surges, continuous high draws, or sudden deviations may indicate failing appliances or wiring issues. Early alerts let you act before bigger damage occurs.
Support Renewable & Battery Integration
If you have solar panels or a home battery, the monitor helps match production and consumption. It can guide when to draw from battery vs grid, or avoid exporting when rates are low.
Raise Awareness & Influences Behavior
Often, simply seeing consumption graphs helps households reduce usage by 5–10%.
Data-Driven Decisions & ROI
Over time, you can analyze how appliance upgrades or behavior changes impacted consumption. This helps you justify investments like HVAC upgrades, insulation, or equipment replacement.
Use Cases: Real Problems a Home Energy Monitoring System Solves
1. Hidden or Phantom Loads
A user discovers via their energy monitor that a poorly insulated fridge draws 200 W continuously even when thought OFF. The monitor helps detect hidden loads that contribute significantly to bills.
2. Faulty HVAC or Overworked Systems
If an HVAC compressor runs unusually long or draws excessive current, the monitor alerts you. Diagnosing early avoids breakdowns or high repair bills.
3. Peak Load Avoidance
In regions with time-of-use pricing, the system helps you avoid drawing peak power (e.g. staggering heavy loads) to reduce demand surcharges.
4. Solar & Battery Management
Homes with solar panels can use the monitor to decide when to use excess power to run appliances, charge battery, or export to grid. It helps maximize self-consumption and minimize grid reliance.
5. Appliance Upgrade Justification
If a new refrigerator or heat pump shows lower consumption immediately, you can calculate ROI, comparing energy saved against cost of replacement.
6. Safety & Electrical Health
Continuous monitoring of currents and deviations may warn of wiring faults, overloaded circuits, or insulation breakdowns—especially helpful in older homes.
How to Choose & Buy a Home Energy Monitoring System
Assess Your Needs & Panel Capacity
Determine how many circuits you want monitored (whole-house or per circuit). Ensure your electrical panel can accommodate CT clamps and space for modules.
Connectivity & Integration
Decide whether you want cloud-based or local operation. If you use a home automation platform like Home Assistant, choose monitors that support open protocols or local APIs (e.g. Shelly, Refoss).
Sampling Speed & Accuracy
Higher sampling rates (e.g. multiple samples per second) yield more accurate data and better disaggregation. Choose systems with good accuracy specs.
Alerting & Anomaly Detection
Check whether the system supports alerts for over-usage, threshold crossing, or fault detection. These features turn passive monitoring into proactive system health coverage.
Firmware & Update Support
Because these systems rely on software, ensure manufacturer/final seller supports firmware updates and security patches.
Warranty & Reliability
Look for multi-year warranties, brand reputation, support availability, and spare part or sensor availability.
Cost & Total Value
Compare cost versus features. A cheaper monitor without alerts or API may not provide much value. Over time, saved energy and insights often justify a higher-quality system.
Purchase Channels
Buy via official brand websites, authorized dealers, or trusted retailers. Avoid grey-market versions lacking firmware updates or activation support.
Installation & Best Practices
-
Turn Off Main Power
Always switch off your home’s main breaker before installing CT clamps or inserting modules. -
Mount CT Clamps on Mains / Circuits
Clamp each conductor properly (only one conductor per clamp, orientation matters). -
Connect to Module / Gateway
Wire CT clamps to your module, connect to its designated terminals. -
Networking / Communication Setup
Connect the module to WiFi, Ethernet, or your smart home bus. Configure with the app or local interface. -
Label Circuits & Calibrate
In the app or interface, label each CT to its circuit (e.g. “HVAC”, “Kitchen”). Calibrate if required. -
Initial Testing & Baseline
Energize, observe live power readings, compare to the utility meter to check consistency. Track baseline over a few days. -
Set Alerts / Thresholds
Configure warnings for high usage, anomalies, or sudden surges. -
Regular Review & Maintenance
Periodically check logs, firmware updates, sensor calibration, and inspect wiring for cleanliness or corrosion.
Summary & Final Thoughts
A home energy monitoring system gives transparency, control, and insight into your electricity usage. It transforms opaque bills into actionable data, letting you optimize, detect faults, and integrate smarter systems like solar or automations.
The product examples (Emporia Vue 3, Shelly Pro EM, Refoss, Tuya WiFi meter, Shelly EM, Square D WISEREMPVZ) provide options spanning full circuit-level monitors, smart home–friendly modules, and ecosystem-driven devices. Match your choice to your home’s complexity, desired integration, and technology preferences.
By installing carefully, labeling correctly, and configuring alerts, you’ll ensure your system starts delivering value immediately. Over time, you’ll understand how your home uses energy, where to cut, and how to shift loads intelligently.
FAQs
Q1: Does a home energy monitoring system save money by itself?
A: Not directly, but by revealing where energy is wasted, it enables you to take action (turn off unused loads, schedule usage, upgrade devices). The system is a tool savings come from how you use its insights.
Q2: Is it safe to install a home energy monitor by myself?
A: Yes, with caution and proper procedures. Always turn off the main breaker, use insulated tools, follow wiring diagrams, and if unsure, hire a qualified electrician. CT clamps and modules are low-voltage once wired but working inside a panel carries risk.
Q3: Can one monitor detect usage of every appliance without sensors on each?
A: Some systems use nonintrusive load monitoring (NILM) to estimate appliance use from overall current waveforms. This can work reasonably well for common loads, but accuracy varies. Using separate CTs per circuit is more reliable.






